Disruptive product innovation represents a paradigm shift in how businesses approach product development and market penetration. It’s not merely about incremental improvements; it’s about creating entirely new markets or disrupting existing ones with groundbreaking offerings. This guide delves into the intricacies of identifying opportunities, developing innovative products, and navigating the challenges inherent in launching and scaling disruptive technologies. We’ll explore both the strategic and tactical aspects, providing a framework for success.
From understanding the characteristics of truly disruptive products to mastering effective go-to-market strategies, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate this complex landscape. We will examine real-world examples of both successful and unsuccessful disruptive innovations, offering valuable lessons learned along the way. The journey from concept to market is fraught with potential pitfalls, but with careful planning and execution, the rewards can be transformative.
Defining Disruptive Product Innovation
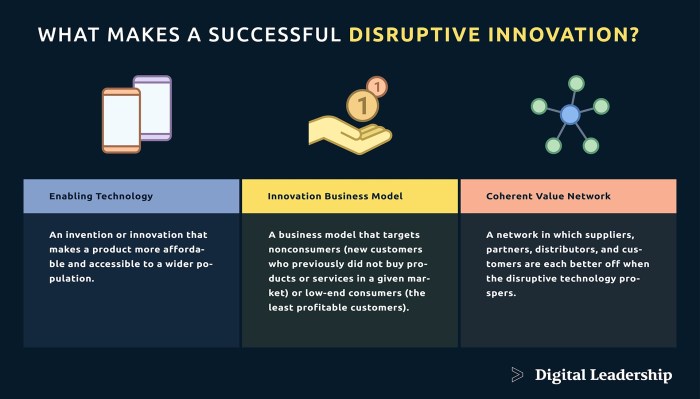
Disruptive product innovation refers to the introduction of a new product or service that significantly alters an existing market or creates a completely new one. Unlike incremental innovations that improve existing products, disruptive innovations often initially appear inferior to established offerings but eventually surpass them, often targeting a different or underserved market segment. This process often involves technological advancements, novel business models, or a combination of both.Disruptive innovations possess several key characteristics.
They typically offer a simpler, more convenient, or more affordable solution compared to existing alternatives, often initially appealing to a niche market. Over time, their performance improves, eventually exceeding the capabilities of established products, leading to widespread adoption and market disruption. Furthermore, disruptive innovations frequently challenge established industry norms and practices, often requiring significant adjustments from both businesses and consumers.
Characteristics of Disruptive Products
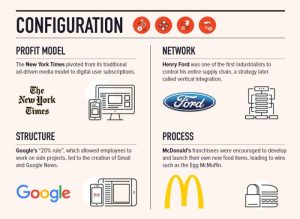
Truly disruptive products are characterized by their ability to create new markets and value networks, eventually displacing established market leaders. They are typically simpler, more convenient, or cheaper than existing alternatives at the outset, even if they initially offer lower performance. This allows them to penetrate new or underserved markets. As technology progresses, the performance of these disruptive products improves, eventually surpassing the capabilities of traditional offerings, leading to widespread adoption.
Examples of Disruptive Innovations
Several examples illustrate the power of disruptive innovation across various industries. The personal computer, initially less powerful than mainframes, disrupted the computing industry. Similarly, digital photography replaced film photography, offering greater convenience and lower costs. In the music industry, digital music platforms like iTunes and Spotify disrupted the traditional music retail model, offering greater accessibility and choice.
Ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft disrupted the taxi industry by leveraging smartphone technology and a more efficient business model. Finally, the emergence of smartphones disrupted the mobile phone industry, integrating numerous functionalities into a single, portable device.
Incremental vs. Disruptive Innovation
Incremental innovation focuses on making gradual improvements to existing products or services. These improvements might enhance performance, add features, or improve efficiency. In contrast, disruptive innovation involves introducing entirely new products or services that often initially seem inferior to existing offerings but eventually surpass them. A comparison can be drawn between the continuous improvement of gasoline-powered cars (incremental) and the emergence of electric vehicles (disruptive), which initially had limited range and charging infrastructure but have improved significantly, challenging the dominance of traditional vehicles.
Stages of Disruptive Innovation
The journey of a disruptive innovation from concept to market typically involves several key stages. The initial stage involves identifying an unmet need or an underserved market segment. This is followed by the development of a minimum viable product (MVP) – a basic version of the product with core functionality – to test the market and gather feedback. Subsequent stages involve iterative development, based on market feedback, to improve the product’s performance and features.
Finally, scaling and widespread market adoption occur once the product demonstrates significant value and competitive advantage. The trajectory of Netflix, initially a DVD rental service by mail, then transitioning to a streaming service, showcases this multi-stage process.
Product Innovation and Product Launch Strategies

Launching a disruptive product requires a well-defined strategy that considers various factors, from market analysis to customer engagement. A successful launch isn’t just about releasing a product; it’s about creating a compelling narrative and delivering a seamless customer experience. This section will explore different launch strategies, provide examples of successful and unsuccessful launches, Artikel a comprehensive go-to-market plan, and discuss best practices for managing customer expectations.
Product Launch Strategy Comparisons: Big Bang vs. Phased Rollout
The choice between a “big bang” launch and a phased rollout significantly impacts a product’s initial reception and long-term success. A big bang launch involves a simultaneous, widespread release across all target markets. This approach generates significant initial buzz but carries higher risk, as any unforeseen issues are immediately amplified. In contrast, a phased rollout involves a gradual release, often starting with a limited beta test or a specific geographic region.
This allows for iterative improvements based on early feedback, mitigating risk and reducing the impact of potential problems. The best approach depends on the product’s complexity, risk tolerance, and market characteristics.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Product Launches
Apple’s iPhone launch in 2007 exemplifies a successful big bang strategy. The massive pre-launch hype, coupled with a compelling product, resulted in immediate market dominance. Conversely, the launch of the Microsoft Zune, a competing MP3 player, is often cited as an example of an unsuccessful big bang launch. Its inferior features and lack of a compelling differentiator led to its quick demise despite the significant initial marketing push.
A successful phased rollout example is the gradual expansion of Tesla’s electric vehicle market, allowing them to refine their production and distribution processes while addressing customer concerns before wider releases.
Go-to-Market Plan for a Disruptive Product
A comprehensive go-to-market plan for a disruptive product should include:
- Market Analysis: Identifying the target audience, their needs, and competitive landscape.
- Value Proposition: Clearly articulating the unique benefits of the product and how it solves a significant problem.
- Marketing Strategy: Defining the marketing channels (e.g., social media, content marketing, paid advertising) and messaging.
- Sales Strategy: Establishing sales channels, pricing strategy, and sales training.
- Customer Support: Developing a robust customer support system to address user inquiries and issues.
- Launch Timeline: Setting realistic timelines for each stage of the launch process.
- Metrics and Measurement: Defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success.
Managing Customer Expectations During Product Launch
Transparency and realistic expectations are crucial for managing customer perceptions during a launch. Clearly communicate the product’s capabilities, limitations, and potential issues. Proactive communication through various channels (e.g., social media, email, blog posts) keeps customers informed and manages their expectations effectively. Responding promptly and empathetically to feedback, both positive and negative, fosters trust and loyalty. Addressing early adopters’ concerns promptly and effectively can shape the overall perception of the product.
Marketing Channels Comparison for Disruptive Product Launch
| Channel | Cost | Reach | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Marketing | Medium (depending on strategy) | High | High (if targeted correctly) |
| Content Marketing (Blog, Articles) | Low to Medium | Medium to High | Medium to High (builds trust and authority) |
| Paid Advertising (Google Ads, Social Media Ads) | High | High | High (but requires careful targeting and optimization) |
| Public Relations | Medium to High | High (potential for significant reach) | Medium to High (depends on media coverage) |
Mastering disruptive product innovation requires a blend of strategic foresight, creative problem-solving, and unwavering adaptability. By understanding the process from ideation to market launch, and by meticulously tracking key performance indicators, businesses can significantly increase their chances of success. While risks are inherent, the potential rewards – in terms of market share, profitability, and long-term competitive advantage – make the pursuit of disruptive innovation a compelling endeavor for any forward-thinking organization.
This guide provides a solid foundation for embarking on this exciting journey.
Key Questions Answered
What is the difference between disruptive and sustaining innovation?
Sustaining innovation improves existing products for existing customers, while disruptive innovation creates new markets and value networks, often initially targeting overlooked or underserved customer segments.
How can I identify unmet customer needs?
Conduct thorough market research, analyze customer feedback, observe customer behavior, and engage in direct customer interviews to uncover unmet needs and pain points.
What are some common reasons why disruptive innovations fail?
Common reasons include underestimating market resistance, inadequate funding, poor execution of the go-to-market strategy, and a failure to adapt to changing market conditions.
How important is user feedback in the development process?
User feedback is crucial. It allows for iterative design improvements, ensures the product meets actual customer needs, and helps identify potential issues before launch.
What are some key metrics for measuring the success of a disruptive innovation?
Key metrics include market share, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, revenue growth, and overall market impact.